What Are the Physics Behind Lens Focusing?
Lenses focus light rays from a point on your object converge onto the image plane. This fundamental principle drives all focusing methods in machine vision. The distance between the lens and sensor where sharp focus occurs is called the mechanicalback focal length. For M12 lenses, this can vary from 1.5mm to 8mm. For C-mount lenses, this distance is not standardized, however, these lenses have a standardized 17.526mm flange focal distance.
In practical terms, focusing adjusts this lens-to-sensor distance to match your working distance. For M12 lenses, each 0.5mm movement (one full rotation) shifts the focus plane by approximately 10-50mm at the object. C-mount lenses achieve focusby moving internal elements via the focus ring and internal opto-mechanical cam system rather than external threading adjustment.
Critical Understanding: Focal Length Terminology
Effective Focal Length (EFL) determines your field of view and depth of field
characteristics. This optical property defines magnification and angular resolution.
Mechanical Back Focal Length is the distance from the last mechanical part of the lens
(typically the rear housing edge) to the image plane. This dimension determines physical compatibility
with your camera system.
Flange Focal Length applies to C-mount systems - it's the
standardized 17.526mm distance
from the C-mount flange surface to the image plane.
Note: Optical back focal length (distance from last optical element to image plane) is
rarely used in camera design. The mechanical back focal length is what determines whether a lens will
physically fit and focus with your camera. Consider Commonlands M12 lenses
for compact applications or C-mount lenses
for standardized flange focal distance systems.

How Do I Focus an M12 Lens?
M12 lens focusing for board level cameras requires systematic adjustment of the threaded mount while monitoring image sharpness. By rotating the lens in its threaded holder, you adjust the back focal length to achieve sharp focus at your working distance. Each full rotation moves the lens exactly 0.5mm due to the standardized M12×0.5 thread pitch.
For the most accurate alignment, consider using ceiling target focusing to eliminate image plane tilt. This tilt issue commonly occurs due to thread tolerance mismatches between M12 lenses and holders, as detailed in our M12 lens technical guide. When lens threads don't perfectly match the holder threads, the lens sits at a slight angle, causing one side of the image to be sharp while the opposite side is blurry. By placing targets on the ceiling above the camera, gravity ensures the sensor and target remain perfectly parallel, eliminating tilt-induced focus gradients across the image.
Mount Camera Securely
Fix the board level camera rigidly, either facing your target or upward for ceiling target method. Even small movements during focusing will affect results.
Position Test Charts
Place four charts at 50% of the image diagonal from center. This reveals any image plane tilt immediately during adjustment.
Illuminate Uniformly
Add consistent lighting across the field of view. Uneven lighting can mask focus issues by creating false contrast gradients.
Set Proper Exposure
Establish correct exposure settings using gray cards before focusing. See our detailed exposure setting guide below for OECF and ColorChecker procedures.
Thread Lens to Focus
Rotate lens in 1/16 turn increments (31.25μm axial movement). Watch for equal sharpness across all test points, not just center.
Lock and Verify
Apply UV+heat dual cure adhesive or use a mechanical lock ring , then verify no focus shift occurred during locking.

⚠️ Professional Tip
Ceiling target focusing is standard practice at Commonlands' camera module assembly facility. Our production lines use precision ceiling fixtures with integrated lighting for consistent, tilt-free focusing across all units. Consider our professional assembly services for production volumes starting at 100 pieces minimum order.
How Do I Focus C-Mount Lenses?
C-mount lenses require a different focusing approach due to their standardized flange focal distance. Unlike M12 lenses that thread directly into holders, C-mount lenses maintain a fixed 17.526mm flange-to-sensor distance with focus achieved through internal optical adjustments via the focus ring.
C-Mount Focus Procedure
- Mount lens to camera: Thread C-mount lens fully into mount until flange contacts. This sets the precise 17.526mm spacing.
- Set aperture: Open to maximum aperture so that you can most precisely set the best working distance during focusing, then stop down to working f-number after focusing.
- Rotate focus ring: Turn the focus ring (not the entire lens) while viewing live image. Most C-mount lenses have ~180-300° of rotation.
- Verify across field: Check center and corners at working aperture. Industrial C-mount lenses should maintain <5% MTF variation.
- Lock focus ring: Tighten set screws on focus ring or apply removable thread locker to prevent drift during operation.
Commonlands offers a comprehensive selection of C-mount lenses optimized for 1/2" to 1" sensors, with focus rings designed for smooth adjustment and reliable locking. These lenses feature low-distortion designs ideal for measurement applications.
How Do I Find Peak Focus Using the Thread-Past Focus Method?
The overshoot-and-return technique ensures you find true peak focus, not a local maximum. By deliberately passing through the point of best focus and then returning with finer adjustments, you verify you've found the global optimum. This method works for both manual adjustment and when reviewing MTF measurement curves.
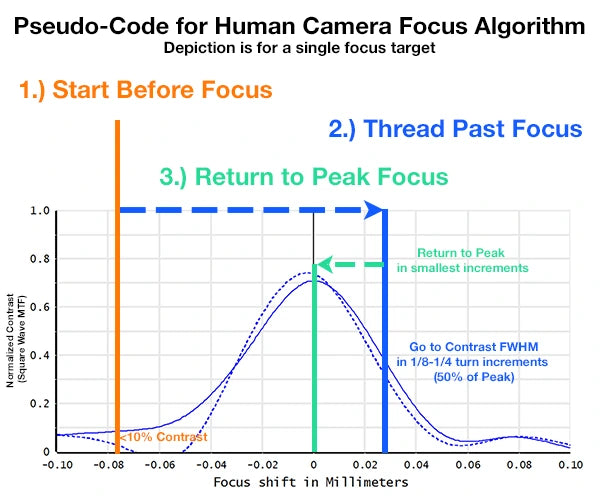
Why Overshoot Works
1. Confirms global maximum: Passing through ensures you haven't stopped at a local peak
2. Provides repeatability: Always approaching from the same direction gives consistent
results
3. Reveals focus curve shape: Understanding the sharpness falloff helps set depth of field
expectations
Which Focus Locking Method Should I Choose?
The choice of focus locking method for board level cameras impacts long-term stability, serviceability, and production throughput. Each method offers distinct advantages for different applications and production volumes when securing board level lenses.
| Method | Cure/Set Time | Strength | Reversible | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV Cure Adhesive | 30-60 seconds | Moderate | No | Indoor/controlled environments |
| UV+Heat Dual Cure | 30s UV + 5min heat | High | No | Automotive, outdoor, high vibration |
| Lock Ring | Immediate | Moderate | Yes | R&D, field-serviceable units |
| PTFE/Teflon Tape | Immediate | Low | Yes | Prototyping, temporary setups |
Commonlands Recommendation
For production volumes, we recommend UV+heat dual cure adhesive applied as a small fillet around the lens-holder interface. This provides maximum environmental resistance while maintaining optical alignment through temperature cycling. Our camera module assembly service includes this professional-grade locking as standard.
How Do I Calculate Depth of Field?
Proper depth of field calculations ensure your entire object range remains in acceptable focus. Visit our Camera Depth of Field Calculator to determine optimal focus settings for your specific lens/sensor combination and working distance requirements.
How Do I Set Proper Exposure Before Assembly?
Correct exposure settings must be established before final focus locking to ensure consistent image quality across production. Using standardized targets like ColorChecker gray patches or OECF charts provides repeatable exposure calibration that eliminates unit-to-unit variation in brightness and contrast.

Simple Exposure Setting Procedure
Position Gray Target
Place an 18% gray card or ColorChecker gray patch at your working distance under production lighting.
Set Standard Illumination
Establish your production lighting conditions. Document lux levels for repeatability across all units.
Adjust Sensor Settings
Target 118 RGB value (46% of 255) for 18% gray. This provides optimal headroom for both highlights and shadows.
Document Settings
Record exposure time, gain, and any ISP parameters. These become your production standards for all modules.
⚠️ Critical for Production
Always set exposure parameters before applying focus lock adhesive. Exposure changes after locking may require different focus positions due to depth of field variations at different f-stops. Commonlands' assembly service includes standardized exposure calibration using professional gray targets as part of our camera module assembly process.
What Are Common Focus Problems and Solutions?
Focus issues cost production time and reduce yield. Understanding root causes enables targeted solutions that maintain long-term stability. Our experience from assembling thousands of camera modules has identified these critical issues and proven solutions.
| Problem | Symptoms | Root Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus Drift | Sharpness degrades over hours/days | Mechanical loosening, weak locking | UV+heat dual cure, proper torque specs |
| Corner Blur | Center sharp, edges soft | Sensor tilt, field curvature | Use ceiling target method, select low-field-curvature lens |
| Material Mismatch | Focus changes with environment | CTE differences, plastic elements | All-glass lenses, matched materials |
| Vibration Loosening | Focus shifts during operation | Insufficient locking torque | Dual cure adhesive + mechanical retention |
| Unit Variation | Each camera needs different focus | Component tolerances stack-up | Active alignment process, tighter QC on components |
Professional Camera Module Assembly Services
Commonlands provides complete camera module assembly with professional focusing services starting at 100 pieces minimum order quantity. Our clean room facilities and precision alignment fixtures ensure consistent, production-ready results for robotics, surveillance, and automotive applications.

Why Choose Commonlands Assembly Services?
- Minimum Order: 100 pieces - ideal for pilot production and small batches
- Ceiling Target Fixtures: Tilt-free alignment eliminating left-right focus gradients
- Professional Locking: UV+heat dual cure standard, custom options available
- Quality Assurance: 100% optical inspection and focus verification
- Volume Scaling: From 100 to 10,000+ units with consistent quality
- Lens Selection: Access to complete M12 and C-mount lens inventory
- Fast Turnaround: 2-3 week standard delivery for most orders

Ready to eliminate focusing challenges? Our team handles the complex alignment process so you can focus on your application. Minimum order quantity: 100 pieces. Learn more about our assembly services or contact our engineers to discuss your requirements.
What Is Active Alignment? (OEM Production Only)
Active alignment optimizes focus while monitoring image quality in real-time, improving yield for high-volume OEM production. This technique is only cost-effective for large production runs due to significant capital equipment costs and complex changeover requirements between different camera models.
When Active Alignment Makes Sense
Minimum Suggested Volume: High-volume OEM production only
Yield Improvement: Increases first-pass yield from ~85% to >98%
Typical Applications: Automotive ADAS cameras, smartphone modules, high-end
surveillance
Equipment Investment: Significant capital costs per alignment station
For lower volumes, manual focusing with proper fixtures and ceiling targets
provides excellent results without the capital investment. Contact Commonlands for
standard assembly services
starting at 100 pieces minimum order quantity.

